CollabLLM: Teaching LLMs to Collaborate with Users for Trustworthy AI
CollabLLM: Teaching LLMs to Collaborate with Users
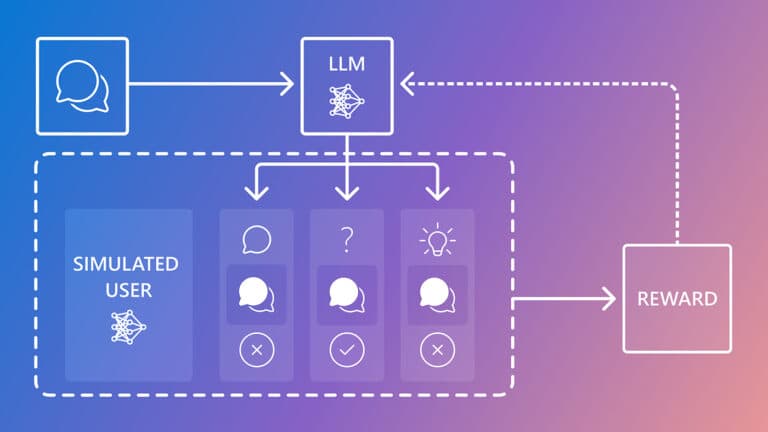
This post introduces CollabLLM, a novel approach developed by Microsoft Research that aims to enhance the collaborative capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) by teaching them to better interact with users. The research focuses on enabling LLMs to understand when to ask clarifying questions, adapt their communication style to different contexts, and ultimately provide a more user-centric and trustworthy AI experience.
Key Innovations of CollabLLM:
- Adaptive Collaboration: CollabLLM trains LLMs to dynamically adjust their tone, communication style, and information-seeking behavior based on user input and situational context. This moves beyond static response generation to a more nuanced and interactive dialogue.
- Intelligent Questioning: A core component of CollabLLM is its ability to identify when user input is ambiguous or incomplete, prompting the LLM to ask relevant questions to gather necessary information. This reduces misunderstandings and improves the accuracy of the LLM's output.
- User-Centric Design: The research prioritizes the user experience, ensuring that the LLM's interactions are natural, helpful, and aligned with user expectations. This involves understanding user intent and providing responses that are not only accurate but also contextually appropriate.
- Trustworthy AI: By fostering more transparent and adaptive communication, CollabLLM contributes to building more trustworthy AI systems. Users are more likely to trust an AI that can explain its reasoning, ask for clarification, and adapt to their needs.
Impact and Applications:
CollabLLM has the potential to revolutionize how humans interact with AI across various domains:
- Customer Service: LLMs equipped with CollabLLM can provide more personalized and effective customer support, understanding user issues more deeply and offering tailored solutions.
- Content Creation: Writers, marketers, and other creative professionals can leverage CollabLLM to collaborate with AI on generating content, receiving more relevant suggestions and feedback.
- Education: AI tutors powered by CollabLLM can offer more adaptive learning experiences, identifying student knowledge gaps and providing targeted explanations.
- Research and Development: Researchers can use CollabLLM to interact with AI models more effectively, accelerating discovery and innovation.
Technical Approach:
While the specific technical details are not fully elaborated in this summary, the research likely involves advanced techniques in reinforcement learning, natural language understanding, and dialogue management. The goal is to train models that can learn from user feedback and continuously improve their collaborative abilities.
Future Directions:
Microsoft Research continues to explore advancements in AI collaboration, aiming to create AI systems that are not just tools but true partners in human endeavors. The development of CollabLLM represents a significant step towards achieving this vision, paving the way for more intuitive, reliable, and human-aligned artificial intelligence.
Related Research Areas:
This work intersects with several key areas of AI research, including:
- Human-Computer Interaction (HCI): Focusing on designing AI systems that are usable, useful, and desirable for humans.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Developing models that can understand, interpret, and generate human language.
- Reinforcement Learning (RL): Training AI agents to make sequences of decisions by learning from rewards and penalties.
- AI Ethics and Safety: Ensuring that AI systems are developed and deployed responsibly, with a focus on fairness, transparency, and accountability.
Conclusion:
CollabLLM is a promising development in the field of AI, addressing the critical need for more effective and trustworthy human-AI collaboration. By teaching LLMs to communicate and learn more like humans, Microsoft Research is pushing the boundaries of what AI can achieve.
Original article available at: https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/research/blog/?lang=fr_ca